What types of windows are there?
Among the different types of windows, the following can be distinguished: windows due to the material (wooden, aluminum, PVC), the way of opening (sash, tilt, sliding), the place of installation (roof windows, facade windows), construction (single and double-leaf , panoramic windows), shape (rectangular, arched), direction of opening, position of the plane of the leaf and the frame relative to each other and other features worth paying attention to when choosing.
Division of windows due to:
Types of windows by material
Types of windows due to the way they open
Types of windows due to the place of assembly
Types of windows due to the structure
Types of windows by shape
Window opening direction
Position of the plane of the sash and the frame relative to each other
Types of windows by material
In terms of the material from which they are made, windows can be divided into:
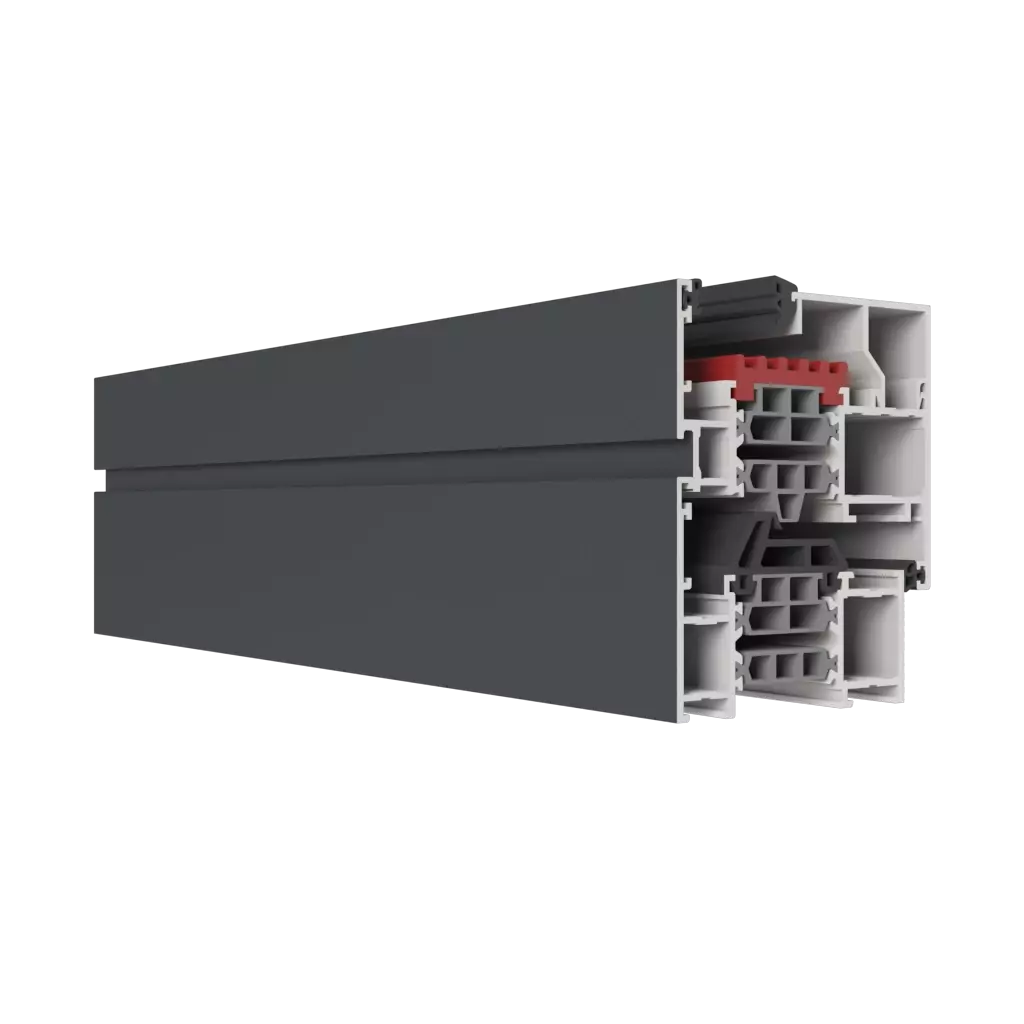
- Plastic windows (PVC, PVC, colloquially PVC) - made of high-impact polyvinyl chloride, characterized by good thermal insulation, durability and easy maintenance, it is recommended to adjust them at least twice a year.
- Wooden windows - they use layer-glued wood, flexible and resistant to changing weather conditions, they require regular care and renovation.
- Aluminum windows - rigid, durable and resistant to external factors, ideal for large glazing, have lower thermal insulation, but modern technologies improve this property.
- Steel windows - used primarily in historic and factory buildings, create a solid structure of almost any shape, are stiff and durable, but do not provide high thermal insulation.
Types of windows due to the way they open
Types of windows due to the way they open are:
- Non-opening windows (FIX) - used in large glazing or in places where ventilation by opening windows is not needed.
- Tilt windows - used where opening the window is impossible or not necessary, for example in sports halls, public buildings and industrial facilities.
- Casement windows - opening inwards (wide) or outwards (English windows).
- Tilt and turn windows - enable full opening or tilting the sash inwards, often chosen in residential and office buildings.
- Side-hinged or tilt-and-turn windows with the function of parallel setting the sash away from the frame - an innovative solution for comfortable and safe ventilation.
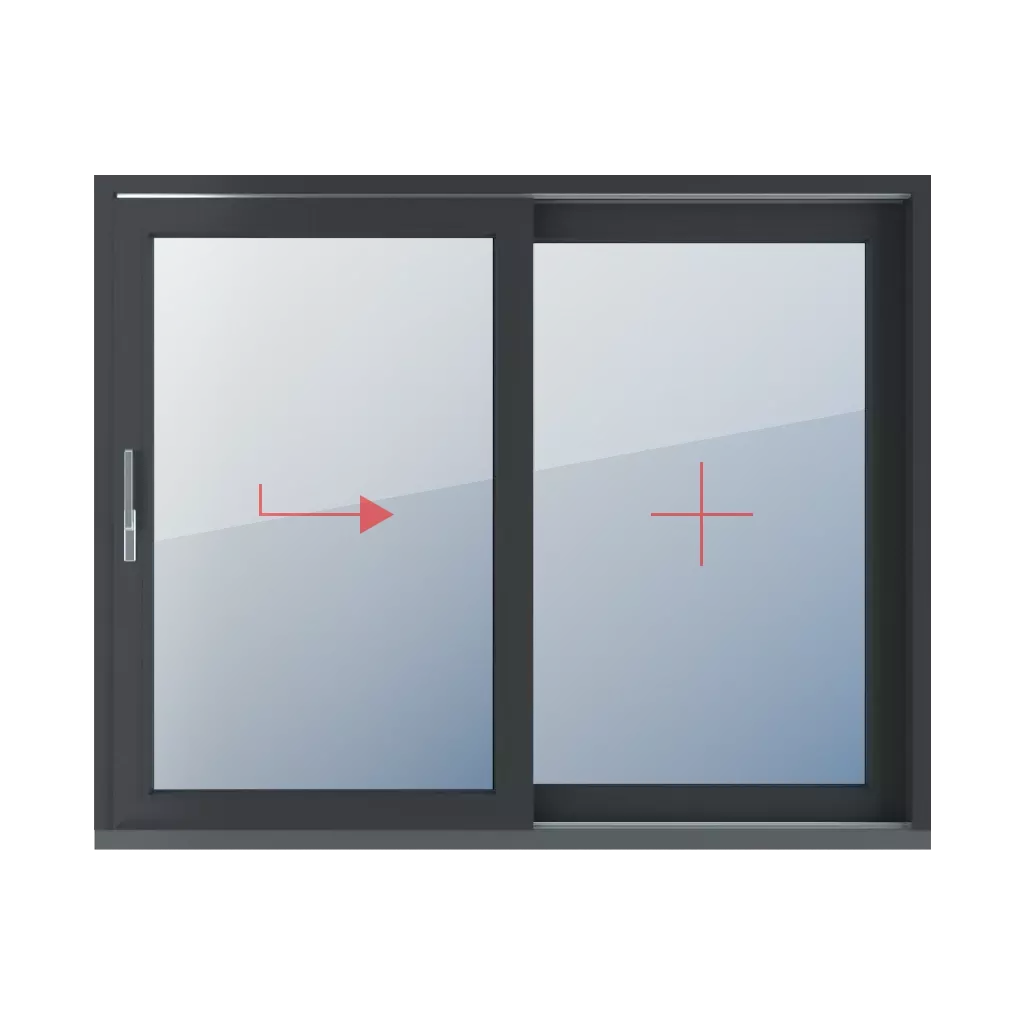
- Sliding windows - often used in terrace windows.
- Tilt and slide windows - they allow you to tilt or open the sash by sliding.
- Pivot windows - found in round windows with the axis of rotation on the level, as well as in rectangular windows.
- Hinged windows - an alternative to standard hinged windows, opened outwards from the bottom, allowing ventilation even during rain.
Types of windows due to the place of assembly
In terms of installation location, windows can be divided into:
- Façade windows - installed in the facade walls of buildings, used to illuminate and ventilate rooms inside the building.
- Roof windows (roof windows) - installed in the roof slopes, allowing the flow of natural light into the attic rooms and ensuring ventilation in this area.
Types of windows due to the structure
Single-frame windows are the most popular and at the same time the simplest to build. However, other types of windows, such as loom windows, casement windows and casement windows, are more characteristic of the older type of construction.
- Single-frame windows are characterized by the construction of a single frame and a single window sash that opens to the inside of the building.
- Loom windows are made of a single casement window that can be fixed or open inwards. This sash is made of a loom that acts as a window frame.
- Frame windows consist of a frame and double window sashes. One of the wings opens to the inside of the building and the other to the outside. Inner wings can be dismantled in the summer season.
- Casement windows are based on a structure made of a loom and a frame, to which double sashes that open inwards are attached. Typically, the outer sashes in casement windows are slightly smaller than the inner sashes.
Types of windows by shape
- Rectangular windows (including square windows) are the most common type of windows, commonly found in various types of buildings.
- Triangular windows are mainly used in buildings with multi-slope roofs, where they fit the characteristic shape of the space.
- Round windows are most often used as glazing or fixed windows. They can be opened in two ways: by rotating the sash around the vertical or horizontal axis, or by tilting it.
- Arched windows have an arched shape and are mainly used in buildings with a unique architectural style, adding elegance and originality to them.
- Trapezoidal windows are trapezoidal in shape and are used when unusual window geometry is required, such as sloping walls or special architectural designs.
Window opening direction
The windows can be divided into left and right windows, depending on the opening direction. This direction is determined by the position of the hinges on the window frame. If we look at the window from the inside of the room and the hinges are on the right side and the handle is on the left, we are dealing with a right window. Similarly, if the hinges are on the left and the handle is on the right, we are dealing with a left window.
Position of the plane of the sash and the frame relative to each other
The arrangement of the sash and the frame in relation to each other has a significant impact on the aesthetics of the window. We can distinguish the following types of windows:
- Non-flush windows - sash and frame do not lie in one plane, creating a spatial effect and clearly marking their shape.
- Half-faced windows - sash and frame partially overlap, but do not form a single plane. This design adds some depth to the window and defines its contours.
- Flush windows - sash and frame are set in one plane, creating a smooth and uniform surface. This type of window is characterized by simplicity and elegance.